Time for a new release of imgflo, the image processing server and dataflow runtime based on GEGL. This iteration has been mostly focused on ironing out various workflow issues, including documentation. Primarily so that the creatives in our team can be productive in developing new image filters/processing. Eventually this will also be an extension point for third parties on our platform.
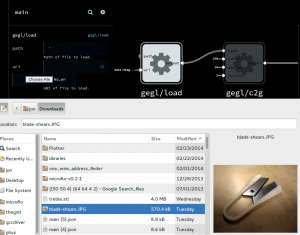
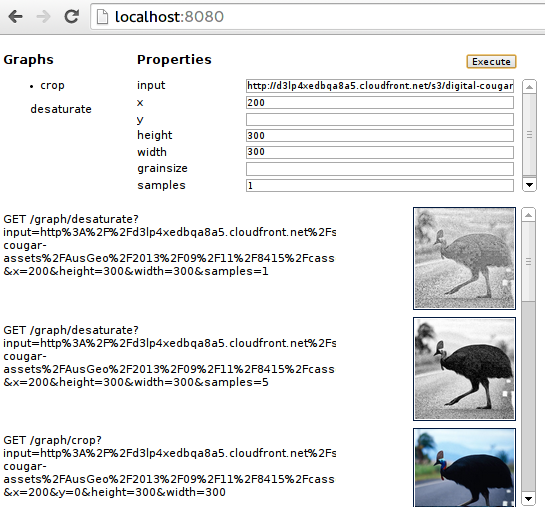
By porting the png and jpeg loading operations in GEGL to GIO, we’ve added support for loading images into imgflo over HTTP or dataURLs. The latter enables opening local file through a file selector in Flowhub. Eventually we’d like to also support picking from web services.
Another big feature is allowing to live-code new GEGL operations (in C) and load them. This works by sending the code over to the runtime, which then compiles it into a new .so file and loads it. Newly instatiated operations then uses that revision of code. We currently do not change the active operation of currently running instances, though we could.
Operations are never unloaded, due both to a glib limitation and the general trickyness of guaranteeing this to be safe for native code. This is not a big deal as this is a development-only feature, and the memory growth is slow.
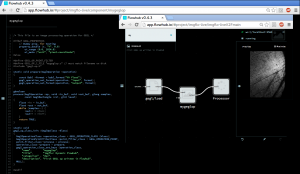
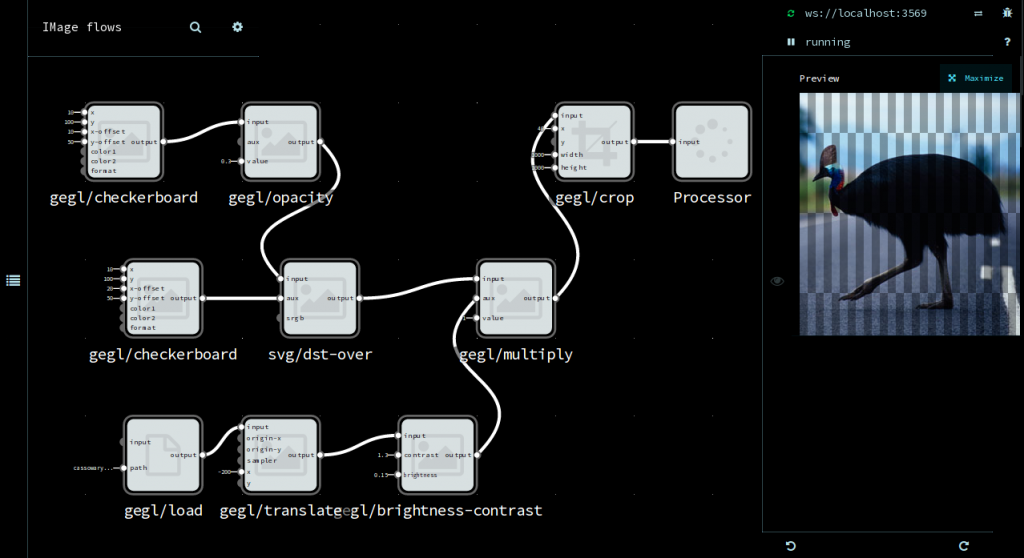
imgflo now supports showing the data going through edges, which is very useful to understand how a particular graph works.
Using Heroku one can get started without installing anything locally. Eventually we might have installers for common OS’es as well.
Vilson Viera added a set of new image filters to the server, inspired by Instagram. Vilson is also working on our image analytics pipeline, the other piece required for intelligent automatic- and semi-automatic image processing.
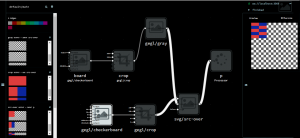
GEGL has for a long time supported meta-operations: operations which are built as a sub-graph of other operations. However, they had to be built programatically using the C API which limited tooling support and the platform-specific nature made them hard to distribute.
Now GEGL can load such operations from the JSON format also used by imgflo (and several other runtimes). This lets one use operations built with Flowhub+imgflo in GIMP:
This makes Flowhub+imgflo a useful tool also outside the web-based processing workflow it is primarily built for. Feature is available in GEGL and GIMP master as of last week, and will be released in GIMP 2.10 / GEGL 0.3.
Next iteration will be primarily about scaling out. Both allowing multiple “apps” (including individual access to graphs and usage monitoring/quotas) served from a single service, and scaling performance horizontally. The latter will be critical when the ~20k+ users who have signed up start coming onboard.
If you have an interest in using our hosted imgflo service outside of The Grid, get in contact.